Rain is a fundamental component of Earth’s hydrological cycle, playing a crucial role in sustaining life on our planet. It is essential for agriculture, maintaining ecosystems, and regulating Earth’s climate. This article delves into the formation of rain, its significance, and the different types of precipitation.
Formation of Rain
The process of rain formation is intricately linked with the water cycle, which involves several stages: evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
- Evaporation: The journey begins with evaporation, where liquid water from oceans, lakes, and rivers is heated by the sun, transforming it into water vapor. This vapor rises into the atmosphere, increasing humidity levels.
- Condensation: As water vapor ascends, it cools down, eventually reaching its dew point. At this stage, condensation occurs, and the vapor transforms back into liquid droplets. These droplets gather around dust particles and other nuclei in the air, forming clouds.
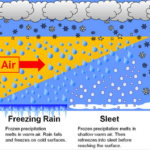
- Precipitation: Within clouds, smaller water droplets collide and merge, growing larger and heavier. Once these droplets become too heavy to remain suspended, they fall to the ground as precipitation, which can take the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
Types of Rainfall
Rainfall can be classified into three main types based on its formation mechanisms:
- Frontal Rainfall: This type occurs when cold air meets warm air in a weather front. The warm air rises over the cold air, cools, condenses, and forms clouds, leading to precipitation. Frontal rainfall is common in temperate regions and can bring persistent, widespread rain.
- Orographic Rainfall: This occurs when moist air is forced to rise over mountains or hills, cooling and condensing to form clouds and precipitation. Orographic rainfall is more pronounced on the windward side of mountains, often resulting in a rain shadow effect on the leeward side.
- Convectional Rainfall: This type occurs when the sun heats the Earth’s surface, causing warm air to rise and cool, leading to condensation and cloud formation. Convectional rainfall is common in tropical regions and during warm weather in temperate zones, often resulting in localized showers.
Importance of Rain
Rain is vital for maintaining Earth’s ecosystems and supporting human activities:
- Agriculture: Rainfall is essential for crop growth and irrigation, influencing agricultural productivity and food security.
- Ecosystems: Rain helps maintain healthy forests, grasslands, and aquatic ecosystems by replenishing water sources and supporting biodiversity.
- Climate Regulation: Precipitation plays a key role in regulating Earth’s temperature by distributing heat around the globe and influencing weather patterns.
Challenges and Opportunities
While rain is crucial for life, its absence or excess can pose significant challenges:
- Droughts: Insufficient rainfall can lead to droughts, affecting agriculture and water availability.
- Flooding: Excessive rainfall can cause flooding, damaging infrastructure and threatening human safety.
To address these challenges, scientists are exploring techniques like cloud seeding to influence precipitation patterns. Cloud seeding involves introducing substances into clouds to enhance precipitation, potentially mitigating droughts or reducing the risk of severe storms.
Conclusion
Rain is a vital component of Earth’s water cycle, supporting life and influencing our environment. Understanding its formation, types, and importance is crucial for managing water resources effectively and addressing the challenges posed by precipitation variability. As we continue to explore ways to manage and predict rainfall, it is essential to appreciate the role rain plays in sustaining our planet’s ecosystems and human societies.
More weather related learning can be found here
Here is what the MetOffice has to say about rain!
Hi I am Marcus, MM0ZIF, a licenced Radio Amateur, Doctor of Musicology, amateur weather enthusiast. I over the years have been a Amateur Radio Tutor, Examiner, and a Regional Manager for the Radio Society of Great Britain.
This site is dedicated more towards Amateur Radio and Weather, with an angle on Technology too. I also maintain https://havenswell.com/ which is my other blog which is more aimed at cooking, hobbies and life in general as well as businness and networking.