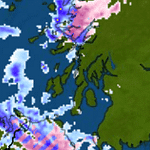
Weather phenomena can be fascinating and sometimes confusing. Two terms that often come up in meteorology are “cyclone” and “anti-cyclone.” While they might sound similar, they are quite different in their formation, characteristics, and impacts. Let’s explore these differences in a fun and educational way!
What is a Cyclone?
A cyclone is a large-scale air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure. Cyclones can be classified into different types, such as tropical cyclones (hurricanes and typhoons) and extratropical cyclones. Here are some key features:
- Low Pressure: Cyclones are characterized by low-pressure centers.
- Rotation: In the Northern Hemisphere, cyclones rotate counterclockwise, while in the Southern Hemisphere, they rotate clockwise. This rotation is due to the Coriolis effect.
- Weather Conditions: Cyclones are often associated with severe weather conditions, including heavy rain, strong winds, and thunderstorms.
What is an Anti-Cyclone?
An anti-cyclone, on the other hand, is a weather phenomenon characterized by a high-pressure center. Anti-cyclones are generally associated with calm and stable weather. Here are the main features:
- High Pressure: Anti-cyclones have high-pressure centers.
- Rotation: In the Northern Hemisphere, anti-cyclones rotate clockwise, while in the Southern Hemisphere, they rotate counterclockwise.
- Weather Conditions: Anti-cyclones typically bring clear skies, light winds, and dry weather.
Key Differences
- Pressure Systems:
- Cyclone: Low-pressure system.
- Anti-Cyclone: High-pressure system.
- Rotation:
- Cyclone: Counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere, clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Anti-Cyclone: Clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere, counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Weather Impact:
- Cyclone: Associated with stormy weather, including rain, wind, and thunderstorms.
- Anti-Cyclone: Associated with calm and clear weather.
- Formation:
- Cyclone: Forms over warm ocean waters or due to atmospheric disturbances.
- Anti-Cyclone: Forms due to the sinking of cold, dry air.
Why Understanding the Difference Matters
Knowing the difference between cyclones and anti-cyclones is crucial for weather forecasting and preparedness. Cyclones can cause significant damage and require early warnings and evacuation plans, while anti-cyclones can lead to prolonged periods of dry weather, which can impact agriculture and water supply.
1: Cyclonic Storms
Cyclonic storms, such as hurricanes, typhoons, and tropical cyclones, are associated with low-pressure systems and can cause significant damage due to:
- Strong Winds: Cyclones can produce extremely strong winds that can uproot trees, damage buildings, and create flying debris.
- Heavy Rainfall: These storms often bring torrential rains, leading to severe flooding, landslides, and water damage to infrastructure.
- Storm Surges: Cyclones can cause storm surges, which are large waves that flood coastal areas, leading to extensive property damage and erosion.
- Tornadoes: In some cases, cyclones can spawn tornadoes, which can cause localized but intense damage.
2: Anti-Cyclonic Storms
Anti-cyclonic storms are associated with high-pressure systems and generally bring fair weather. However, they can still cause damage, albeit in different ways:
- Drought: Prolonged periods of high pressure can lead to dry conditions and droughts, which can severely impact agriculture, water supply, and increase the risk of wildfires.
- Heatwaves: Anti-cyclones can cause heatwaves, leading to health risks such as heatstroke and dehydration, and can strain energy resources due to increased demand for cooling.
- Air Quality: Stagnant air in high-pressure systems can lead to poor air quality, trapping pollutants and causing respiratory issues.
Key Differences in Damage
- Cyclonic Storms: Cause immediate and often severe damage due to wind, rain, and storm surges. The impact is usually sudden and can be catastrophic.
- Anti-Cyclonic Storms: Cause more gradual damage through prolonged dry spells, heatwaves, and poor air quality. The impact is less immediate but can be widespread and long-lasting.
Understanding these differences helps in preparing for and mitigating the impacts of these weather phenomena. For more detailed information, you can visit resources like the National Weather Service and the World Meteorological Organization
Learn More
For more detailed information on cyclones and anti-cyclones, you can visit the National Weather Service and the World Meteorological Organization.
- 6.4: Cyclones and Anticyclones – Geosciences LibreTexts
- Cyclones And Anticyclones: What Is The Difference? (ownyourweather.com)
- Anticyclonic storm – Wikipedia
- 11.7: Cyclones – Geosciences LibreTexts
Stay Informed!
Keep checking MM0ZIF Radio for more insightful articles on weather phenomena and other exciting topics. Don’t forget to tune in to our broadcasts for the latest weather updates and expert insights.
Hi I am Marcus, MM0ZIF, a licenced Radio Amateur, Doctor of Musicology, amateur weather enthusiast. I over the years have been a Amateur Radio Tutor, Examiner, and a Regional Manager for the Radio Society of Great Britain.
This site is dedicated more towards Amateur Radio and Weather, with an angle on Technology too. I also maintain https://havenswell.com/ which is my other blog which is more aimed at cooking, hobbies and life in general as well as businness and networking.